The Voices of Bharat: Statistical Insights into India's Language Diversity

India, often called Bharat, is a land of vibrant cultures, profound history, and an astonishing tapestry of languages. As you traverse this incredible nation, you are met with a symphony of diverse voices, accents, and dialects, each telling a unique story. At Zoice, a conversational AI platform for India, we understand that truly connecting with Bharat means embracing and understanding this rich linguistic landscape.
Languages in India: A Statistical Snapshot
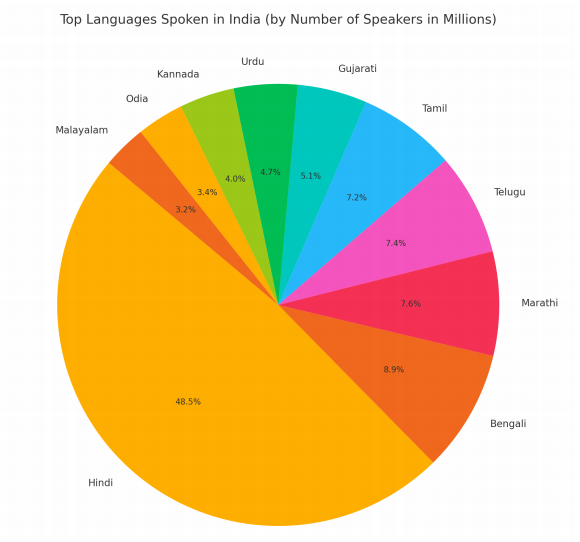
The linguistic richness of India is both astonishing and awe-inspiring. While India has 2 official languages, 22 scheduled languages, the country is also home to an impressive 121 languages and 270 mother tongues. Among these, Sanskrit stands out as one of the world's oldest languages. This linguistic mosaic reflects India's diverse and pluralistic society, where people from various religions, ethnicities, castes, and classes coexist and interact.
Let's delve into the top languages spoken across India and their geographical footprint:
- Hindi: As one of the official languages of India, Hindi is the most widely spoken language in the country, with 528.3 million speakers. It serves as a supplemental language in many federal recruitment exams and is predominantly spoken across states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, and Delhi. Hindi is descended from Sanskrit and has been influenced by Dravidian, Arabic, Portuguese, English, Persian, and Turkish languages. It also encompasses many dialects like Awadhi, Braj, Khadi Bhasha, Bhojpuri, and Haryanvi.
- Bengali: India's second most spoken language, Bengali has 97.2 million speakers. It is primarily spoken in the Indian states of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Assam, and Tripura, and is also found in countries like Bangladesh, The Middle East, the United States, Australia, Japan, the United Kingdom, and Canada. Bengali evolved from Indo-Aryan languages, particularly Sanskrit, over more than 1,300 years.
- Marathi: With 83.0 million speakers, Marathi is India's third most widely spoken language. This Indo-Aryan language is the official language of the western states of India, including Goa and Maharashtra. Marathi is known for its approximately 42 dialects.
- Telugu: A Dravidian language, Telugu is spoken by 81.1 million people in India, primarily in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Yanam (Puducherry). The Government of India has recognized Telugu as one of the six classical languages of India. It boasts a rich history with approximately 10,000 inscriptions as of 1996.
- Tamil: Also from the Dravidian language family, Tamil is spoken widely in Tamil Nadu and neighboring South Indian states. It is the official language of both Singapore and Sri Lanka and is often considered one of the world's oldest living languages, with a literary history spanning over 2,000 years.
- Gujarati: An Indo-Aryan language derived from Sanskrit, Gujarati is the official language of Gujarat, a state in northwest India, and is spoken by 55.4 million people. It is divided into three dialects: Parsi, Hindu, and Muslim.
- Urdu: Spoken by 50.7 million people in India, Urdu is an official language in West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Telangana, and Jharkhand, and also the official language of Pakistan. Like Hindi, Urdu is a Hindustani language and is written from right to left using an extension of the Persian script, which is an extension of the Arabic alphabet.
- Kannada: A Dravidian language, Kannada is spoken by 43.7 million people in India, mainly in Karnataka and other South Indian states. It has more than 20 dialects and was designated a classical language of India.
- Odia: The official language of Odisha, Odia is spoken by 37.5 million people in India. It is the sixth Indian language to be classified as a Classical language due to its long literary tradition and minimal borrowing from other languages.
- Malayalam: Spoken by around 34.8 million people in India, primarily in Kerala, Puducherry, and Lakshadweep, Malayalam also traces its roots to the Dravidian languages. It shows variations in intonation patterns, vocabulary, and grammatical and phonological elements based on geography, religion, community, occupation, social strata, style, and register.
This vibrant linguistic landscape also gives rise to language mixing, such as the widespread use of 'Hinglish' (a blend of Hindi and English), though specific statistics for 'Hinglish' are not provided in the sources. This influence of various languages on Hindi itself, and the presence of numerous dialects within languages like Marathi and Kannada, demonstrate this dynamic mixing.
Key Insight
India is home to 2 official languages, 22 scheduled languages, 121 languages, and 270 mother tongues, with 70-75% of Indians not understanding English, making multilingual AI solutions essential for effective customer engagement.
Communication in India: Beyond the Numbers
While a significant portion of India communicates in its regional languages, English plays a crucial role. Along with Hindi, English is one of India's federal government's official languages and is the official language in some Indian states like Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh. English has been taught in Indian schools since the 1800s. However, as much as 70-75% of Indians do not understand English and rely on Hindi or other regional languages to communicate.
This highlights the vital need for multilingual support in services, especially in customer care. Indian inbound call centers, globally recognized as powerhouses, have impressively adapted to this need. While their initial growth was driven by English proficiency, major centers now offer multilingual support in French, Spanish, German, Italian, Portuguese, and several Asian languages, allowing global companies to consolidate customer support in India. This linguistic versatility ensures effective communication with a global and diverse domestic clientele.
AI and the Future of Indian Languages
The linguistic diversity of India presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses seeking to connect with their audience. This is where AI-powered solutions become transformative. Indian inbound call centers are at the forefront of AI integration, blending human expertise with artificial intelligence to enhance service efficiency and customer experience.
Here's how AI is revolutionizing language services in India:
- Text and Voice Translators / AI Voice Agents: Conversational AI technologies are now widely used for initial customer interaction triage, routing, and handling routine inquiries. For example, AI systems can resolve up to 40% of customer issues without human intervention, seamlessly transferring complex cases to human agents. This includes AI-powered phone agents that can autonomously manage appointments, answer frequent customer questions, and even drive sales through natural-sounding conversations.
- Multilingual Data Extraction Systems & Analytics: AI is used for real-time analytics, providing agents with customer sentiment analysis and next-best-action recommendations. Leading Indian call centers utilize sophisticated quality management technologies that employ AI call assistance to automatically analyze 100% of calls, identifying training opportunities and compliance issues. This helps extract valuable insights from multilingual interactions.
- Real-time Agent Assistance: AI provides agents with suggested responses, compliance alerts, and knowledge base access during customer interactions, enhancing efficiency and quality.
- Scaling Multilingual Support: AI language technologies can handle basic inquiries in multiple languages, ensuring consistent automated service regardless of agent location, while routing complex issues to appropriate human agents.
Core Components
- AI Voice Agents Handle routine inquiries in multiple Indian languages
- Multilingual Data Analytics Extract insights from interactions in various languages
- Real-time Agent Assistance Provide language support for human agents
- Hybrid Approach Blend AI and human intelligence for optimal service
At Zoice, we are committed to harnessing these advancements. Our platform enables businesses to implement AI-powered phone agents that can seamlessly handle inbound and outbound calls, complementing existing call center operations. This hybrid approach, combining human intelligence with technological sophistication, ensures an optimal blend of empathy, problem-solving, and operational efficiency, significantly improving customer satisfaction.
Implementation Roadmap
- 1Analyze your customer base's language preferences
- 2Implement AI-powered phone agents for basic multilingual support
- 3Develop language-specific training for human agents
- 4Integrate analytics to identify language-based patterns
- 5Continuously refine AI models with regional language data
The future of customer service in India will be defined by increased AI integration, analytics-driven personalization, and omnichannel expertise. By leveraging platforms like Zoice, businesses can truly tap into the diverse "Voices of Bharat," connecting with customers in their preferred languages and dialects, and fostering deeper engagement and loyalty.
Ready to Transform Your Customer Service?
Discover how Zoice's conversation intelligence platform can help you enhance CLV and build lasting customer loyalty.